The Fantastic Thiomargarita It is the largest bacteria ever discovered. Its existence has been known since 2009, but only recently was it possible to confirm the fact that it consists of a single cell, and that it is about 50 times larger than any other known bacteria. Recently discovered published in the scientific journal Sciences It is further evidence of how limited our knowledge of bacteria is and their huge diversity.
T. Magnifica It was first identified in 2009 by biologist Olivier Gros, while he was exploring and studying life forms among mangrove Guadeloupe, the archipelago of the French Antilles located in the Caribbean. Among the fallen leaves from trees and rotting in the standing water beneath the mangroves, Gross noticed strange filamentous creatures, about an inch long and thus visible to the naked eye. At first he thought that it could be a fungus or another type of organism belonging to eukaryotes, the most complex field of living organisms that includes animals, including humans.
Later, Gross conducted new microscopic analyzes and came to the conclusion that he was not facing eukaryotes, but something else. However, it took nearly ten years before other research groups in California paid more attention to the new organism, analyzing and observing it with various techniques, including electron microscopy that allows for large magnifications.
In 2018, confirmation came that it was a single cell, and the fruit of those observations became preliminary research published last February. Now, a few months later, the study has been published in the scientific journal Scienceswhich is of great interest among those who deal with bacteria and beyond.
T. magnifica under an electron microscope (Olivier Gros/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory)
What amazes research groups is that T. Magnifica It consists of a single large filamentous cell, so long that it can be observed with the naked eye, which is rare for bacteria. In the center of the bacteria is a vacuole, a fluid-containing vesicle limited by a membrane, along the edges of which are other membranous structures which seem to have properties similar to organelles, the structures of eukaryotic cells necessary for their survival. The research team called it ‘bibini’: ‘from the Vulgar Latin ‘pipe’ used to refer to the concept of small.
Observe some samples from T. MagnificaThe research team also observed that the bacteria’s genetic material was encapsulated in hundreds of thousands of peppers, rather than being free inside the cell as is usually the case with most bacteria. Each of these bipenes also contains ribosomes, which are the structures responsible for decoding genetic information to produce proteins.
However, it is not yet clear whether albinos all contain the same set of genetic material, proteins and ribosomes, because at the moment the research group has sequenced the entire cell, while it has not yet been possible to devote more in-depth analyzes of their individual structures. Some peppers may have different functions than others, but only new insights can provide some answers.
The research group also wants to understand whether T. Magnifica It is typical exclusively for Guadeloupe and the ecosystems in which it is observed, among the mangroves, or if it is also found in other regions of the world. However, the presence of large amounts of sulfur appears to be crucial, given that these bacteria feed on their particles.
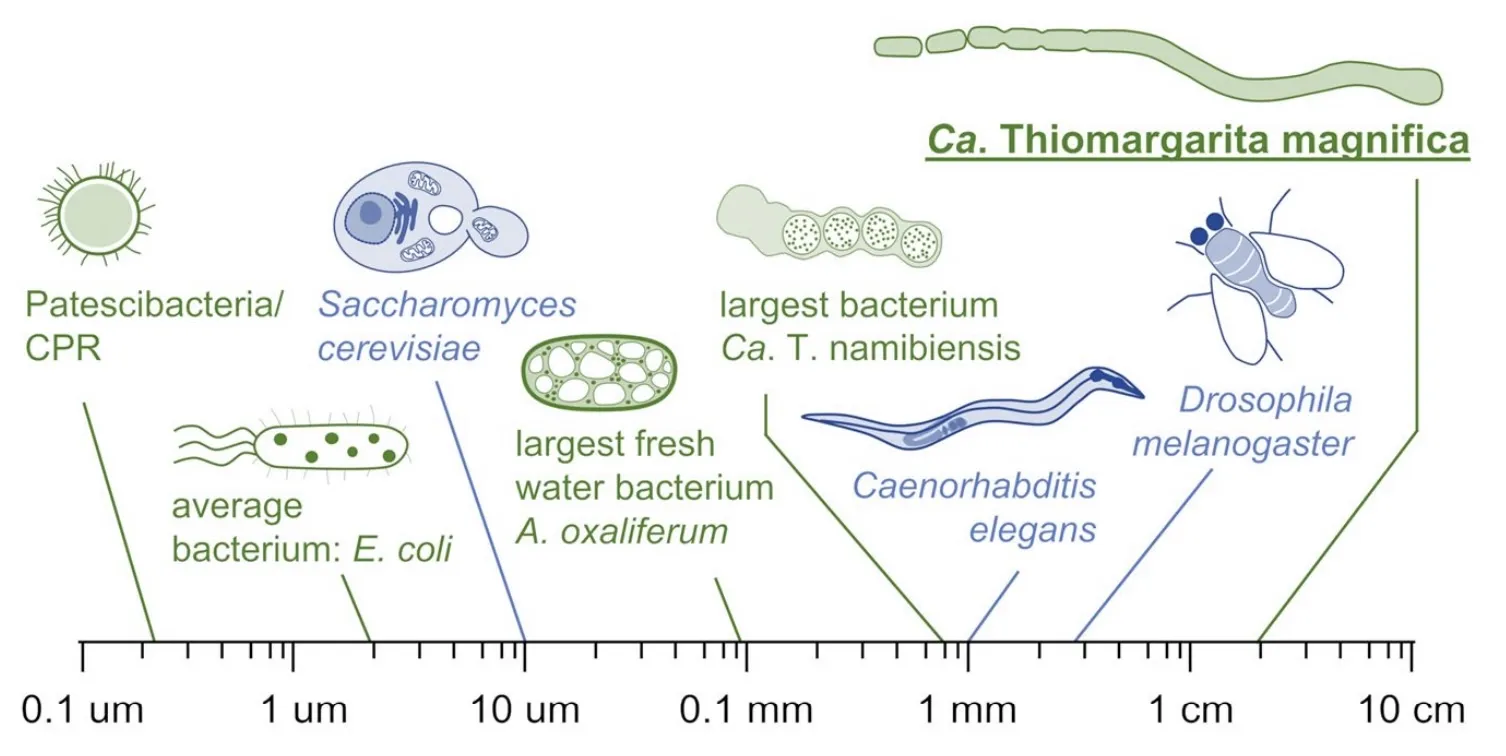
Size of T. magnifica compared to other species (Science)
Discovery T. Magnifica However, it confirms hypotheses about the existence of bacteria much larger than those identified so far, and could pave the way for useful new research to better understand their properties.
After all, there is no shortage of work in this field: research turning point In 2016 it was estimated that there are hundreds of billions of different types of bacteria around the world and that 99.999% of them have yet to be discovered. Although not everyone agrees with this estimate, there is widespread consensus among researchers that only a tiny fraction of all bacteria on our planet have been identified so far.

“Incurable internet trailblazer. Troublemaker. Explorer. Professional pop culture nerd.”







More Stories
Aston Martin DBX: More changes inside than outside
This malware eludes antivirus software on Windows, and is very dangerous: how to overcome it
Perfect wardrobe with accessories: You can find it at IKEA and it costs less than 40 euros