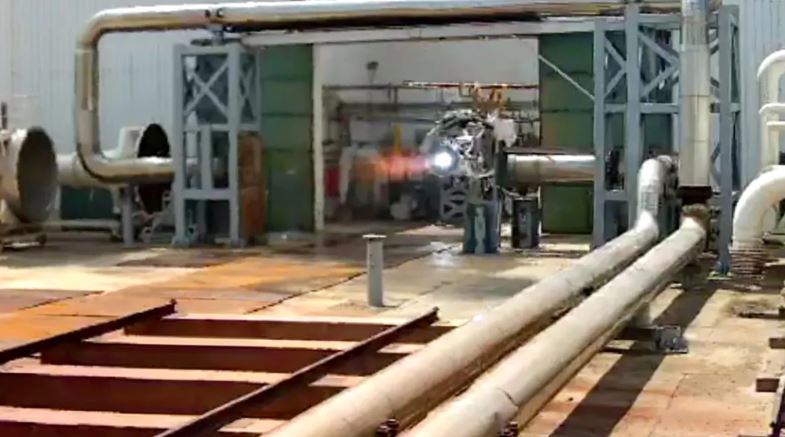
there China It has taken another step towards its ambition to carry out a manned lunar mission after a new test successfully engine Its very heavy missile. Technical difficulties have been overcome in the prototype of the YF-79 rocket engine, which will be used in manned lunar and interplanetary flights, according to its developer, Beijing Aeronautics Institute of Technology (BAEIT).
On September 30, three ground tests of the new hydrogen-oxygen engine were successfully completed, according to BAEIT, a unit of the state-owned China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), the main contractor for the village’s space program. BAEIT said it conducted 12 ignition tests in a week for the new engine, as well as a high-thrust hydrogen-oxygen engine and an orbital check engine, without giving further details.
The 25-ton YF-79 rocket is being developed for the Long March 9, an ultra-heavy rocket designed for space missions, such as manned moon landings and Mars exploration. Its developers aim to make the YF-79 the most powerful rocket engine of its kind, capable of multiple ignition and powering a lander on its final stage.
Last year, CASC completed major steps in the development of the second stage engine for the Long March 9: YF-90, a 220-ton supplemental combustion cycle hydrogen-oxygen engine.
The Long March 9 is designed with the capacity to carry 15 to 50 tons of payload to the Moon, or 12 to 44 tons to Mars, Liu Bing, a designer at CASC, said at the Zhuhai Air Show last year. Its low Earth orbit capacity is between 50 and 140 tons, compared to the 150 tons of the US SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket and about six times the capacity of the Long March 5, currently China’s most powerful rocket, weighing 25 tons.
After the Chang’e spacecraft collected 5 samples from the lunar surface in 2020 during an unmanned mission, China plans to send astronauts to the moon within a decade and build a permanent lunar station by 2035.

“Internet trailblazer. Travelaholic. Passionate social media evangelist. Tv advocate.”






More Stories
A strong geomagnetic storm was reported in Europe, as well as in Italy
The LEGO 10341 NASA Artemis Space Launch System isn't the first of its kind
12 out of 20 regions do not guarantee basic levels