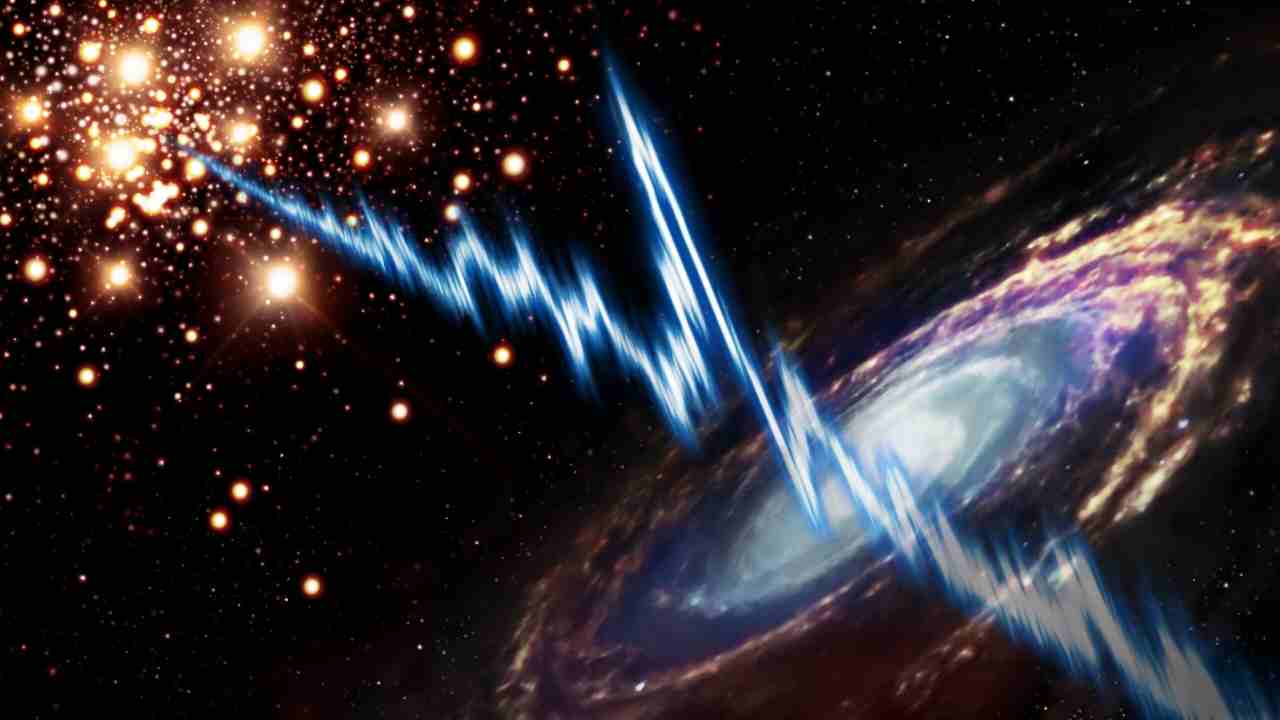
A radio explosion was recently detected near Earth. As Ansa writes, this is the closest radio flash ever detected to our planet, even 40 times closer than any other flash observed so far.
It was called lightning FRB 20200120E, It was located exactly in The Sun is 12 million light-years away from Earth. After it exploded in an unexpected area, “a globular mass full of old stars – as the Italian news agency wrote – not as small and huge as expected.”

New Near-Earth Lambo Radio: The Closest Ever Discovered
According to rumors in the scientific community, such a discovery could have a very important impact as possible Changing the way to search for these phenomena and above all to study these phenomena, radio flashes, which were discovered only a few years ago. The issue was published in an article in Nature and later also in Nature Astronomy, and to highlight it was an international group of experts, in which some researchers also participated. National Institute of Astrophysics (INAF). The radio burst in question is repeated over time, and its source is in Bod Galaxy (M81 or NGC 3031)In the direction of the constellation Great Bear. In an effort to better study the radio burst with the highest possible accuracy and sensitivity, scientists have used measurements from 12 different telescopes Forming part of the European VLBI Network (EVN), then combining it with data from other telescopes.
They also participated several antennas Including the INAF radio telescopes: the radio telescopes of Medicine (Bologna) and Noto (Syracuse) in the VLBI mode, the Sardinia radio telescope (Cagliari) as a single dish and the VLBI. According to the insider’s conclusion, the FRB 20200120E fast radio flash should be It comes from a highly magnetized neutron star, They were formed as a result of the collapse caused by the accretion of a white dwarf or by the merger of merged stars into a binary system. Kenzi NemoThe researcher at Astron and the University of Amsterdam and first author of the Nature Astronomy paper, commented on the discovery: “Diameter.” And again: “Some of the signals we measured are very short and strong. This suggests that we do see a magnetar, but in a place that has not been found before.”

“Internet trailblazer. Travelaholic. Passionate social media evangelist. Tv advocate.”






More Stories
From Earth to the Moon at the speed of light: Watch the chilling video
Watch what the planets were like 3.8 billion years ago, video (chilling reconstruction)
The origin of 469219 Kamo'oalewa has been revealed